Summary Card
Definition of Hypertelorism
An increase in the interorbital distance between the dacryons.
Classification of Hypertelorism
Tessier classification is based on interorbital distance. The standard is 20-30mm.
Causes of Hypertelorism
Syndromic (Apert's, Crouzens, Edwards) or non-syndromic (facial clefts, midline tumours).
Treatment of Hypertelorism
An MDT to restore orbital dystopia and cosmesis through box osteotomy, facial bipartition, and medial canthopexy.
Definition of Hypertelorism
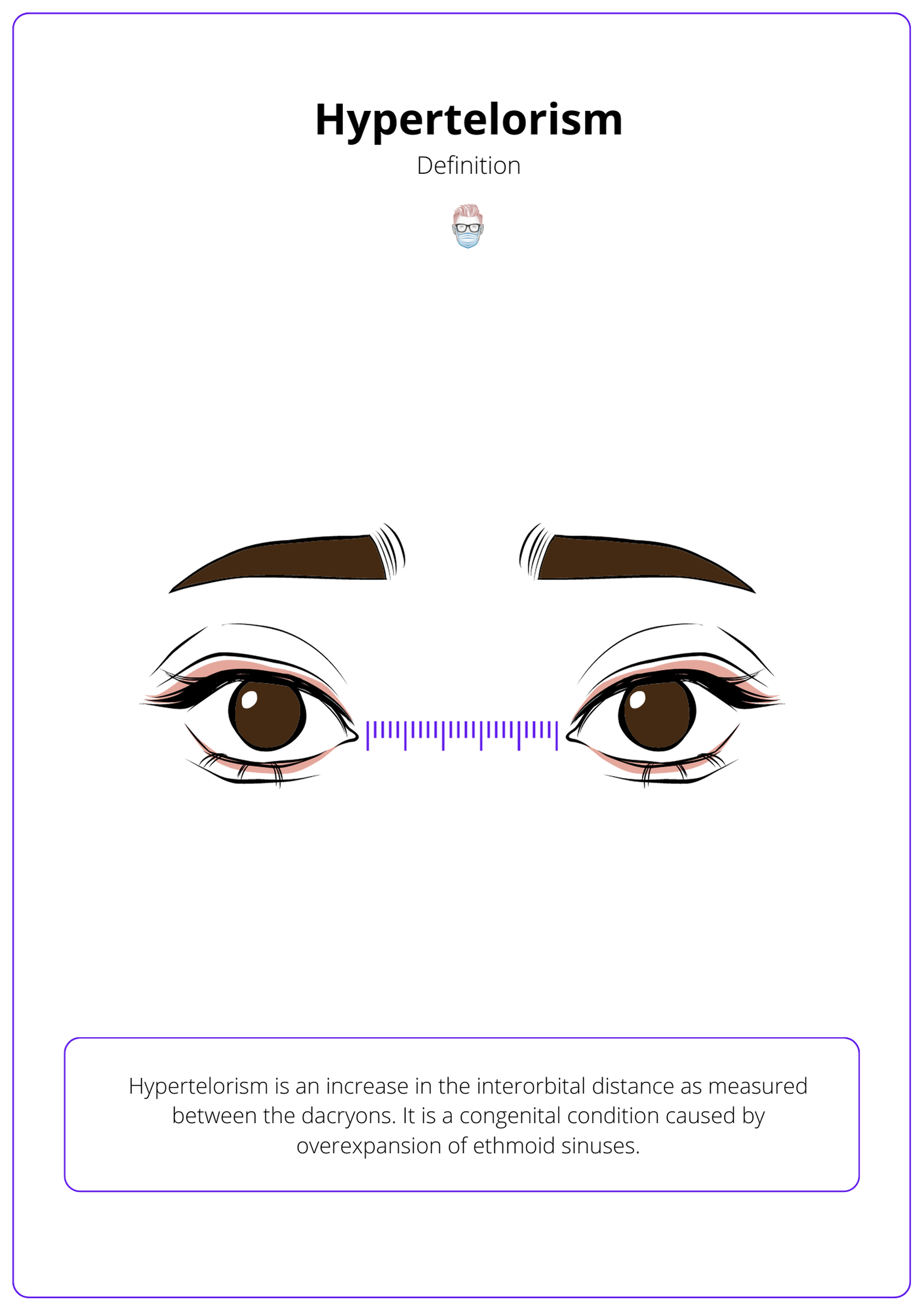
Hypertelorism is an increase in the interorbital distance as measured between the dacryons. It results in true lateralization of the orbit where the inner canthal distance (ICD), the outer canthal distance (OCD), and interpupillary distance (IPD) are all increased.
It is a congenital condition caused by overexpansion of ethmoid sinuses. See image below for further clarification.
Classification of Hypertelorism
Hypertelorism is defined radiologically by the distance between the dacryons, with classifications provided by Tessier, and is distinct from similar conditions like telecanthus and pseudo-hypertelorism.
Hypertelorism is a measurement from the dacryon. This is the junction between the maxillary, frontal, and lacrimal bones. It is a radiological measurement, not a clinical measurement.
The average adult interorbital distance can range from 20-30mm. Tessier provides a classification of this, as detailed below in the illustration.

It is important to be aware of two other similar conditions:
- Telecanthus: increases the intercanthal distance with the normal distance between the bony orbits.
- Pseudo-hypertelorism: 'illusion' of telecanthus in patients with a flat nasal bridge or prominent epicanthal folds. This is linked to Down Syndrome, Fetal Alcohol Syndrome, and Klinefelter Syndrome.
Causes of Hypertelorism
Hypertelorism, characterized by an increased distance between the eyes, can be caused by syndromic conditions like Apert's syndrome or non-syndromic factors such as sincipital encephaloceles.
Hypertelorism can be syndromic or non-syndromic:
- Syndromic: Apert's, Craniofrontonasal dysplasia, Crouzens, Edwards.
- Non-syndromic: Sincipital encephaloceles, facial clefts, midline tumours.
An example of hypertelorism is seen in the illustration below of a patient with craniofrontonasal dysplasia.

Treatment of Hypertelorism
Treatment of hypertelorism involves a multi-disciplinary approach focused on restoring function and normal appearance through surgical techniques such as box osteotomy, facial bipartition, and medial canthopexy.
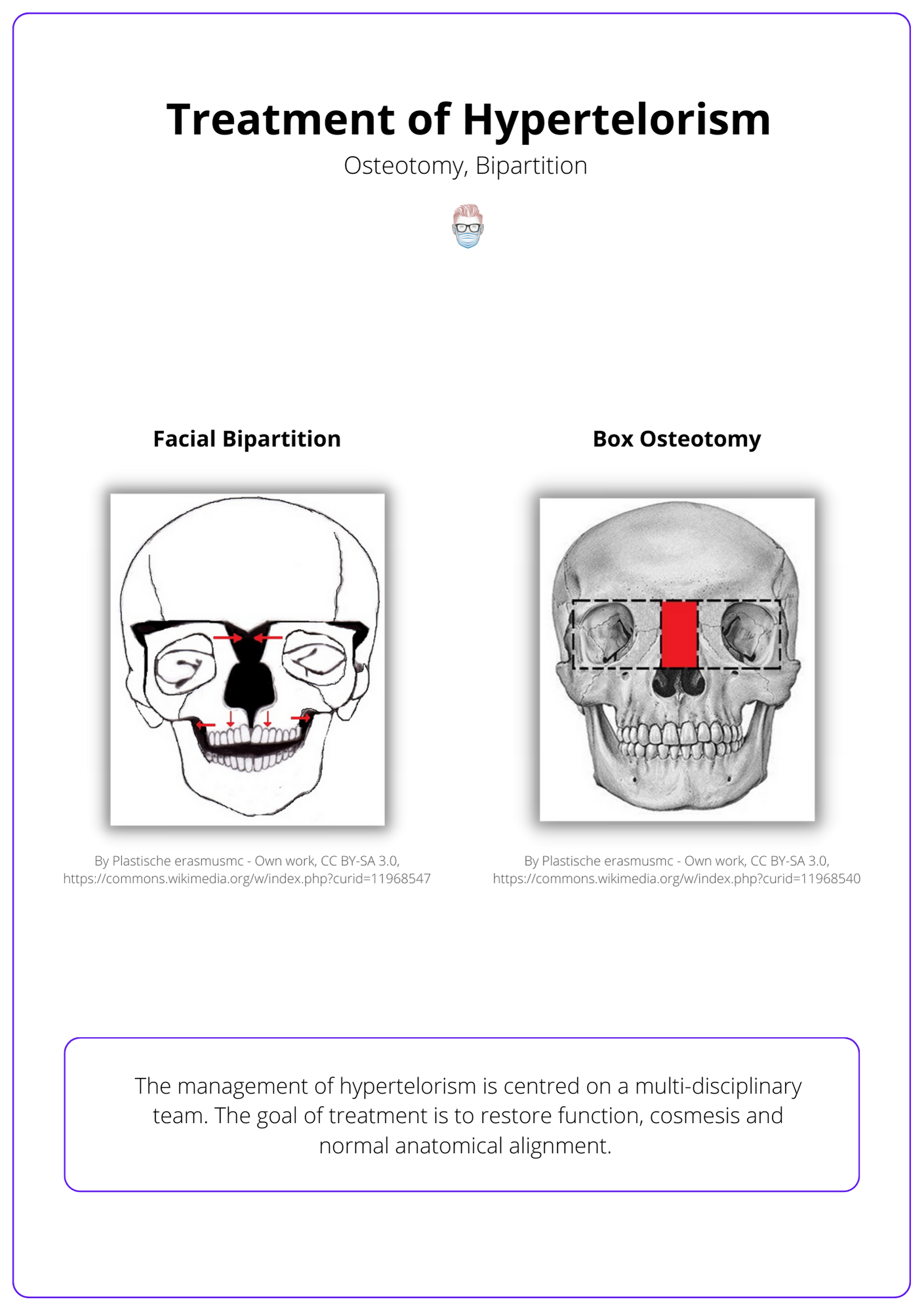
The management of hypertelorism is centred on a multi-disciplinary team. The goal of treatment is to restore function, normal orbital dystopia, cosmesis, and normal anatomical alignment.
Surgical techniques that can be considered are:
- Box Osteotomy: normal midface width and hypertelorism
- Facial Bipartition: an inverted V deformity of maxillary occlusion.
- Medial Canthopexy: reattach the medial canthal ligament after osteotomies.
Surgery is often indicated between the ages of 5 - 7. This is to reduce the risk of damage to unerupted teeth or maxillary growth.
These surgical treatments for hypertelorism are visualised below.
Conclusion
1. Understanding Hypertelorism: You have gained a comprehensive understanding of what hypertelorism is, including its definition as an increase in the interorbital distance measured between the dacryons.
2. Learning the Classification System: You are now familiar with the Tessier classification system, which categorizes hypertelorism based on interorbital distance, providing a standard measurement range.
3. Identifying the Causes: You've learned about the various causes of hypertelorism, distinguishing between syndromic causes like Apert's, Crouzen's, and Edwards syndromes, and non-syndromic causes such as facial clefts and midline tumors.
4. Treatment for Hypertelorism: You've explored the multi-disciplinary treatment approaches for hypertelorism, including surgical techniques like box osteotomy, facial bipartition, and medial canthopexy, aimed at restoring orbital dystopia and improving cosmesis.


